Guide to FFmpeg
From converting formats to real-time streaming, this article explains FFmpeg’s capabilities, its relevance in modern innovation workflows, and how to apply it effectively in both technical and strategic contexts.
Table of Contents
- What is FFmpeg?
- Core Features of FFmpeg
- Use Cases in Innovation and Tech Management
- How FFmpeg Works: Step-by-Step Guide
- Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
- Resources
What is FFmpeg?
FFmpeg is an open-source command-line tool used to process video, audio, and other multimedia files and streams. It’s widely respected for its speed, flexibility, and broad compatibility. Built on libraries like libavcodec, libavformat, and libavfilter, FFmpeg is used by major players like Google, Netflix, and Adobe.
Core Features of FFmpeg
Format Conversion
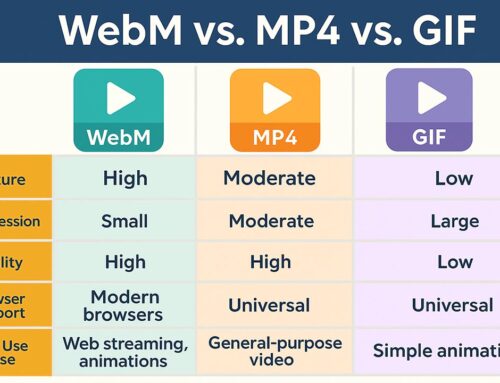
FFmpeg supports nearly every codec and container format, including MP4, AVI, MKV, MOV, WebM, and FLV. It’s capable of converting between formats efficiently, which is critical in content repurposing workflows.
Example:
ffmpeg -i input.mov output.mp4Streaming Capabilities
FFmpeg can encode live video and stream it over networks using protocols like RTMP, HLS, and MPEG-DASH. This makes it essential for live event broadcasting, surveillance systems, and remote learning platforms.
Example:
ffmpeg -f lavfi -i testsrc -f flv rtmp://live.example.com/app/streamFiltering and Effects
Through its powerful filtergraph system, FFmpeg enables tasks like resizing, cropping, overlaying text/images, deinterlacing, and applying video effects.
Example:
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vf "scale=1280:720" output.mp4Use Cases in Innovation and Tech Management
Product Development
FFmpeg accelerates prototyping of multimedia apps and services. Developers can quickly test different media handling features, compressions, and delivery mechanisms.
Media Workflows
In content-driven organizations, FFmpeg automates repetitive tasks such as transcoding video assets, generating thumbnails, or synchronizing subtitles.
Data-Driven Decisions
By extracting metadata and media analytics, teams can evaluate user engagement and content performance.
Example:
ffmpeg -i video.mp4 -f ffmetadata metadata.txtHow FFmpeg Works: Step-by-Step Guide
Installing FFmpeg
- macOS:
brew install ffmpeg - Ubuntu:
sudo apt install ffmpeg - Windows: Download binaries from https://ffmpeg.org
Basic Commands
- Extract audio:
ffmpeg -i video.mp4 -q:a 0 -map a audio.mp3- Capture screenshot:
ffmpeg -i video.mp4 -ss 00:00:10.000 -vframes 1 screenshot.pngAdvanced Commands and Automation
- Batch Convert All
.avi to.mp4
for f in *.avi; do ffmpeg -i "$f" "${f%.avi}.mp4"; done- Overlay watermark:
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -i logo.png -filter_complex "overlay=10:10" output.mp4Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
-hwaccel cuda).
Final Thoughts
FFmpeg is not just a media tool—it’s a backbone technology for innovation in video and audio applications. Its flexibility, performance, and open-source nature make it a strategic asset for developers, media technologists, and product managers. Whether you’re building new digital products, optimizing workflows, or exploring AI-driven content analysis, FFmpeg provides a reliable and powerful foundation.








Leave A Comment